Gold code
A Gold code, also known as Gold sequence, is a type of binary sequence, used in telecommunication (CDMA)[1] and satellite navigation (GPS).[2] Gold codes are named after Robert Gold.[3] Gold codes have bounded small cross-correlations within a set, which is useful when multiple devices are broadcasting in the same range. A set of Gold code sequences consists of 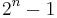 sequences each one with a period of
sequences each one with a period of 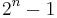 .
.
A set of Gold codes can be generated with the following steps. Pick two maximum length sequences of the same length 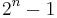 such that their absolute cross-correlation is less than or equal to
such that their absolute cross-correlation is less than or equal to 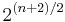 , where
, where  is the size of the LFSR used to generate the maximum length sequence (Gold '67). The set of the
is the size of the LFSR used to generate the maximum length sequence (Gold '67). The set of the 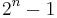 exclusive-ors of the two sequences in their various phases (i.e. translated into all relative positions) is a set of Gold codes. The highest absolute cross-correlation in this set of codes is
exclusive-ors of the two sequences in their various phases (i.e. translated into all relative positions) is a set of Gold codes. The highest absolute cross-correlation in this set of codes is  for even
for even  and
and 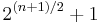 for odd
for odd  .
.
The exclusive or of two Gold codes from the same set is another Gold code in some phase.
Within a set of Gold codes about half of the codes are balanced — the number of ones and zeros differs by only one.[4]
See also
- Kasami code
- Complementary sequences
- Space Network - a NASA system that uses Gold codes
References
- Inline references
- ^ George, M., Hamid, M., and Miller A. Gold Code Generators in Virtex DevicesPDF (126 KB)
- ^ GPS - explained (Signals)
- ^ Dr. Robert Gold
- ^ Holmes, p.100
- General references
- Gold, R. (1967), Optimal binary sequences for spread spectrum multiplexing (Corresp.), IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13 (4), pp. 619–621.
- Holmes, J.K. (2007), Spread Spectrum Systems for GNSS and Wireless Communications, Artech House, Norwood, ISBN 978-1-59693-083-4.
|
||||||||||||||||||||